In
the intricate world of pharmaceuticals, every pill, capsule, or vial of
medicine begins its journey as a carefully crafted concoction of various
components. At the heart of this intricate process lies a fundamental element
known as the “drug substance” or “active pharmaceutical ingredient” (API). In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the
significance of drug substances in pharmaceutical manufacturing, exploring
their definition, importance, manufacturing process, regulatory aspects, and
the evolving landscape of drug substance development. Join us on this in-depth
journey to uncover the critical role that drug substances play in delivering
safe and effective medicines to patients worldwide.
 |
| Figure 01- Drug Substance in Pharmaceuticals |
This
article is to be driven with the below mention details;
|
o o o o o
o o o o o o |
What is Drug Substance?
A drug substance, also known as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), is the main chemical in a pharmaceutical product that is in charge of producing the therapeutic action. The bioactive element is what delivers the intended medicinal benefit. Depending on the kind of medication being made, drug ingredients may be found as tiny molecules, peptides, proteins, or nucleic acids.
The
Significance of Drug Substances
The
importance of drug substances in pharmaceutical manufacturing cannot be
overstated. They are the building blocks upon which the entire drug formulation
process relies. Here are some key elements, why drug substances are crucial:
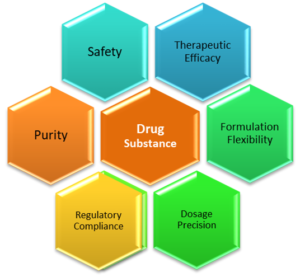 |
| Figure 02: Significance of Drug Substances (Key Elements) |
1. Therapeutic Efficacy
Drug
substances are the primary agents responsible for the intended therapeutic
effect of a medication. They interact with specific biological targets, such as
receptors or enzymes, to produce the desired clinical outcome.
A
key factor in determining a drug’s importance in the fields of pharmacology and
medicine is therapeutic efficacy. It refers to a drug’s capacity to exert the
desired therapeutic result, efficiently controlling or curing a particular
medical condition while minimizing side effects. As it directly affects patient
outcomes and quality of life, a drug’s efficacy is a key component of its
clinical value. Preclinical and clinical trials are used in the rigorous
examination of therapeutic efficacy during the drug development and evaluation
procedures to make sure a material used to make medications helps patients as
intended. The importance of a drug substance ultimately depends on its capacity
to deliver dependable and successful therapeutic solutions, making it a key
component in the development of contemporary medicine.
2. Dosage Precision
Precise
control over the quantity and quality of the drug substance is essential to ensure
accurate dosing in the final drug product. Even minor variations can have
significant implications for patient safety and efficacy.
In
the world of pharmaceuticals, dosage accuracy is of utmost importance, To
ensure that patients receive appropriate dosage of a treatment for their
condition. It refers to the precise and accurate measurement and administration
of pharmaceutical drug substance / Drug product. Precision in dosage is
critical for several reasons: it enhances the effectiveness of treatment by
ensuring that the therapeutic dose is consistently delivered, minimizes the
risk of adverse side effects due to overdose / under-dosing, & it promotes
patient safety by reducing the potential for medication errors. Dosage accuracy
is essential for maximizing therapeutic results and raising standards of care
generally in the era of personalized medicine & more complex drug regimens.
3. Safety and Purity
The
purity and quality of the drug substance directly impact the safety of the
medication. Rigorous testing and quality control measures are in place to
detect and eliminate impurities or contaminants.
When
we talk about drug compounds; safety & purity are crucial. When a drug
substance is considered safe, it must not harm the patient when taken in
accordance with the recommended dosage.. Testing and evaluation of potential
side effects, toxicity & interactions with other medications are required
for this. In contrast, purity indicates to the lack of contaminants or
impurities in the drug substance that could affect its safety and efficacy.
To
achieve consistent treatment results and to reduce the danger of unanticipated
adverse responses, high levels of purity must be maintained.. In order to
protect patient health and the effectiveness of medical treatments, safety
& purity are important concepts that guide the creation, production, and
regulatory licensing of pharmacological substances.
4. Formulation Flexibility
Drug
substances can be formulated into various dosage forms, such as tablets,
capsules, injections, or topical creams, providing versatility in drug delivery
to suit patient needs.
In
the context of pharmacological components formulation flexibility is of utmost
importance in pharmaceutical development. It refers to the capacity to modify
and improve a drug product’s composition and design to satisfy particular
therapeutic objectives, patient needs, and manufacturing specifications.
Due
to their ability to formulate drugs in such a way; that is both effective &
practical for patients, pharmaceutical companies can improve patient compliance
and treatment result. Adjustments can be made in dosage forms; release
profiles, and administration methods, allowing for a variety of patient
demographics and disease states to be addressed.. The ability to fine tune
therapeutic products for improved safety, efficacy, patient satisfaction play a
crucial role in drug development study;
5. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory
agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, impose stringent requirements / regulations
on drug substances’ quality, manufacturing and documentation. Compliance with
these regulations is essential for market approval.
In
the context of pharmacological components formulation flexibility is of utmost
importance in pharmaceutical development. It refers to the capacity to modify
and improve a drug product’s composition and design to satisfy particular
therapeutic objectives, patient needs, and manufacturing specifications.
Due to their ability to formulate drugs in a
way that is both effective and practical for patients, pharmaceutical companies
can improve patient compliance and treatment outcomes. Adjustments can be made
to dosage forms, release profiles, and administration methods, allowing for a
variety of patient demographics and disease states to be addressed. The ability
to fine-tune therapeutic products for improved safety, efficacy, and patient
satisfaction plays a crucial role in drug development.
The
Manufacturing Process of Drug Substances
The
manufacturing of drug substances is a highly specialized and tightly controlled
process. It typically involves the following stages:
 |
| Figure 03- Manufacturing of Drug Substances |
1. Chemical Synthesis or Extraction
The
production of drug substances often begins with chemical synthesis / extraction
from natural sources. In the case of chemical synthesis, organic chemistry
techniques are employed to create the desired compound with high purity.
Extraction, on the other hand, involves isolating the compound from natural
sources like plants or microorganisms.
Chemical
synthesis / extraction plays a pivotal role in the manufacturing process of
drug substances. In chemical synthesis, pharmaceutical chemists meticulously
design and execute reactions to create the desired molecular structure of the
active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) from starting materials. This method
allows for precise control over the composition & purity of the drug
substance. On the other hand, extraction involves isolating the API from
natural sources such as plants or microorganisms. It harnesses the power of
selective solvents / techniques to extract and purify the target compound. Both
approaches are crucial in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring the production
of safe and effective drug substances that form the foundation of countless
medications.
2. Purification
Purification
steps are critical to removing impurities and contaminants. Techniques such as
chromatography, crystallization, and filtration are used to achieve the
required level of purity.
Purification
is a critical step in the manufacturing process of drug substances / Active
pharmaceutical ingredients (API), ensuring that the final product meets the
highest standards of quality, safety & efficacy. This essential phase
involves the removal of impurities, contaminants and unwanted by-products.
These may have been generated during earlier stages of synthesis extraction.
Various techniques, such as chromatography, crystallization, filtration, and
distillation, are employed to isolate and refine the desired compound, resulting
in a highly pure and pharmaceutically active substance. The meticulous
purification process not only enhances the therapeutic effectiveness of the
drug but also ensures compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, making
it a fundamental aspect of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
3. Characterization
Thorough
characterization of the drug substance is essential to ensure its identity,
quality, and consistency. Analytical methods such as spectroscopy,
chromatography, and mass spectrometry are employed for this purpose.
Characterization
is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for drug substances / Active pharmaceutical ingredients (API). It
involves the comprehensive analysis & understanding of the chemical,
physical and biological properties of the
active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). This step ensures that the drug
substance is consistently of high quality, purity & potency, meeting
stringent regulatory standards / safety requirements / norms. Characterization
encompasses various techniques, such as spectroscopy, chromatography & mass
spectrometry, to identify & quantify impurities. These techniques confirm
the molecular structure and assess the stability of the API throughout its
production. The data generated through characterization is vital in
establishing robust manufacturing processes, determining appropriate storage
conditions and ensuring the safety and efficacy of the final drug product.
Ultimately, a thorough characterization process is fundamental for maintaining
product quality and patient safety in the pharmaceutical industry.
4. Formulation Development
Once
the drug substance is obtained in its pure form, pharmaceutical scientists work
on developing the final dosage form. This involves selecting suitable
excipients & determining the optimal formulation for administration.
Formulation
development is a critical phase in the manufacturing process of drug substances
/ API. This phase involves the systematic design & optimization of a drug’s
composition and manufacturing methods to ensure safety, efficacy, stability and
patient acceptability. During this stage, pharmaceutical scientists
meticulously select the appropriate ingredients, evaluate their compatibility
and fine-tune their ratio, to create a stable and effective drug product. The
goal is to achieve a formulation that not only meet the regulatory standards /
requirements but also facilitates efficient & reproducible manufacturing
processes. Formulation development plays a pivotal role in translating a drug
substance in-to market-ready product, serving as the foundation for subsequent
clinical trials and commercial production, ultimately improving patient access
to safe and effective medications.
5. Quality Control
Quality
control measures are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. This
includes in-process testing, stability testing, and final product testing to
verify the drug substance’s quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Quality
control is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for drug substances /
API. It encompasses a systematic set of procedures /measures designed to ensure
that the produced drug substance consistently meets predefined quality
standards and specifications. This involves rigorous testing and analysis at
various stages of production, from raw material inspection to intermediate
processing steps and the final product. Quality control procedures include
assessing the chemical composition, purity, potency & physical attributes of the drug substance.
Adherence to strict quality control protocols not only guarantees the safety
& efficacy of the drug but also ensure compliance with regulatory
requirements/norms, safeguarding public health and maintaining the reputation
of pharmaceutical manufacturers.
6. Regulatory Oversight
The
pharmaceutical industry is subject to rigorous regulatory oversight to ensure
the safety & efficacy of drug
substances and final drug products. Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food
and Drug Administration (USFDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have
established guidelines / requirements that manufacturers must need to adhere
to. Manufacturers are required to submit extensive documentation on drug
substance quality, manufacturing processes and safety data as part of the
regulatory approval process. This ensures that the drug substance meets
stringent quality standards & poses no undue risks to patients.
Regulatory
oversight plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, efficacy and quality of
drug substances. It encompasses a comprehensive framework of laws, regulations
and agencies that supervise every aspect of drug substance development and
manufacturing. This oversight is significant as it safeguards public health by
rigorously evaluating the chemical, biological, and pharmacological properties
of drug substances, setting stringent quality standards, and monitoring
compliance throughout the drug’s lifecycle. Regulatory bodies like the FDA in
the United States or the EMA in Europe are entrusted with the responsibility of
evaluating data, conducting inspections, and granting approvals, instilling
confidence in healthcare professionals and patients that the drug substance/API
they are using meets the highest standards of safety / effectiveness..
Lean more…..
1. Pharmaceutical Drug substance (API) and Drug
Product: Definition
2. What are Sartans (A family of Medicine)
3. N-Nitrosamine impurities: An overview for
Pharmaceutical Drug Substance and product
4. Drug Substance and Drug Product Manufacturing
Flow: Discovery to Delivery
5. What is Pharmaceutical Management system for
Pharmaceutical Industries

