Pharmaceutical science covers a diverse field focused on the
discovery,
development, and evaluation of drugs intended for medical purposes. It is the combination of
elements of biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and technology to formulate
medications that enhance human health effectively.
From initial Research and
Formulation to Clinical Trials and Regulatory Approval, pharmaceutical
scientists play a crucial role in every stage of drug
development.
Their efforts not only tackle existing health issues but also
drive forward medical innovation, striving to expand treatment choices and
improve global quality of life.
In
continuation to introduction of Pharmaceutical science, we can say it is a
broad field with several specialized branches.
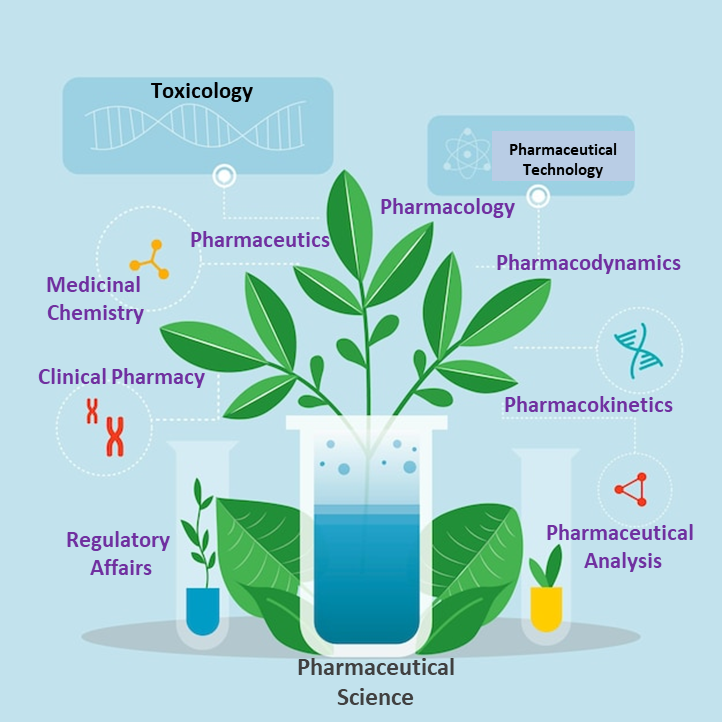
Pharmaceutical science is a TREE 🌳🌳 have some key branches 🎋, each contributing uniquely to its comprehensive field of study:
Pharmacology:
Pharmacology is the study 🕮 of the
effects of drugs on biological systems. It encompasses the study of drug
action, mechanisms of action, therapeutic uses, and adverse effects. This
field plays a crucial role in drug development, ensuring medications are
effective, safe, and tailored to treat specific diseases or conditions.
Pharmacologists investigate the impact of drugs on
organs, tissues, and cells to optimize dosages and minimize adverse effects.
· Pharmaceutics:
Pharmaceutics focuses 👀 on the development, formulation, and manufacturing of pharmaceutical dosage forms such as tablets, capsules, injections, creams, and ointments. It involves understanding drug delivery systems and optimizing their efficacy, safety, and stability.
It covers the study of drug formulation, drug
delivery systems, and the physical and chemical properties of drugs.
Medicinal Chemistry:
A specialized field within
pharmaceutical science that combines chemistry, biology, and pharmacology to
design, develop, and synthesize pharmaceutical agents. It focuses on
understanding the chemical structures and properties of drugs to optimize their
efficacy, safety, and specificity.
Medicinal chemistry involves the design, synthesis, and optimization of
biologically active compounds (drugs) for therapeutic use. Medicinal chemists
strive to discover new drugs, improve existing medications, and understand
their structure-activity relationships.
 |
| Medicinal Chemistry |
Pharmacokinetics:
Pharmacokinetics is the study of
how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated by the body.
It plays a crucial role in determining the dosage regimens and therapeutic
monitoring of drugs.
It explores the time course of drug
concentration in the bloodstream and tissues, influenced by factors such as
dosage, route of administration, and patient-specific variables like age and
health condition.
Pharmacodynamics:
Pharmacodynamics explores the
biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, including their
mechanisms of action, receptor interactions, and dose-response relationships.
It focuses on understanding the relationship
between drug concentration and its pharmacological effects, including
mechanisms of action, receptor interactions, and biochemical pathways involved.
Pharmacodynamics principles help elucidate drug efficacy, potency, and the
onset and duration of therapeutic effects.
Toxicology:
Toxicology investigates the
adverse effects of drugs and chemicals on living organisms. It involves
studying the toxicity mechanisms, dose-response relationships, and risk
assessment of pharmaceuticals and environmental toxins.
It encompasses the study of toxins, poisons, and
other harmful agents, exploring their mechanisms of action, absorption,
distribution, metabolism, and excretion in the body
 |
| Toxicology |
Pharmaceutical Analysis:
Pharmaceutical analysis involves
the qualitative and quantitative assessment of pharmaceutical
substances and dosage forms to ensure their identity, purity, potency, and
stability. Analytical techniques such as chromatography, spectroscopy, and mass
spectrometry are commonly used in pharmaceutical analysis.
Clinical Pharmacy:
Clinical pharmacy focuses on the
safe and effective use of medications in patient care. Clinical pharmacists
work directly with healthcare providers and patients to optimize drug therapy,
prevent medication errors, and monitor for adverse drug reactions.
Clinical pharmacists also educate patients
about their medications, including proper administration techniques and
potential side effects. Their expertise extends to areas such as
pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and therapeutic drug monitoring,
contributing to improved patient outcomes and healthcare quality.
 |
| Clinical Pharmacy |
Pharmaceutical Technology:
Pharmaceutical technology
encompasses the development and application of advanced technologies in drug
delivery, manufacturing, and quality control. It includes areas such as
nanotechnology, bio pharmaceutics, and process optimization.
Pharmaceutical technologists employ advanced
techniques in drug formulation, drug delivery systems, and manufacturing
processes to ensure the stability, efficacy, and safety of medications.
Regulatory Affairs:
Regulatory affairs professionals
ensure that pharmaceutical products comply with regulatory requirements and
standards set by government regulatory
agencies. They are responsible for obtaining regulatory approval for drug
development, manufacturing, labeling, and marketing.
Regulatory affairs professionals also stay
updated on evolving regulations and industry trends to facilitate timely
approvals and ensure adherence to global regulatory requirements.
The branches of pharmaceutical science collectively form a broad interdisciplinary approach, covering crucial aspects such as drug discovery, development, manufacturing, and usage.
By integrating knowledge from biology, chemistry, pharmacology, engineering, and regulatory affairs, pharmaceutical science facilitates the discovery of new treatments, improves existing therapies, and addresses unmet medical needs. Together, they form a comprehensive framework that drives advancements in healthcare and enhances therapeutic outcomes for patients worldwide.
Learn More………..
Research and Development: Definition
Pharmaceutical Drug substance (API) and Drug Product: Definition